India’s startup ecosystem, the world’s third-largest with 195,065 DPIIT-recognized ventures fueling a $450 billion digital economy, demands more than rote learning—it craves creators, risk-takers, and innovators. Yet, traditional curricula, mired in memorization and exam-centric drudgery, churn out job-seekers, not job-makers, with only 10% of graduates deemed employable for entrepreneurial roles, per NASSCOM. Enter the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, a visionary blueprint mandating experiential learning, vocational integration, and critical thinking to nurture entrepreneurial mindsets from school to university. By 2025, with 50% of learners exposed to vocational education and interdisciplinary curricula rolling out nationwide, campuses like IITs and IIMs are evolving into startup forges, birthing 5,000+ spin-offs and 1.5 million jobs.
Backed by Atal Innovation Mission’s (AIM) 2,500 tinkering labs and Startup India’s Rs 945 crore Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS), this overhaul isn’t optional—it’s essential for Viksit Bharat. Drawing from UGC guidelines, NEP implementation reports, and founder insights, this article dissects how India’s curriculum must—and is—changing to build entrepreneurial grit. Cling to the old ways, and you’ll hobble the next Zomato or Ola.
Table of Contents
The Entrepreneurship Deficit: Why India’s Curriculum Needs a Revolution
India graduates 1.5 million engineers annually, yet 80% lack problem-solving skills, per ASER reports, stifling the 195,000 startups hungry for innovative talent. Pre-NEP curricula emphasized theory over practice, fostering fear of failure in a culture where 90% youth prefer stable jobs over entrepreneurship. NEP 2020 flips this: By 2025, foundational literacy and numeracy (FLN) by Grade 3, vocational exposure for 50% learners, and a 5+3+3+4 structure prioritize holistic development, creativity, and skills like coding, AI, and financial literacy from Class 6. States like Karnataka and Assam lead implementation, with 100% GER targets and industry-linked internships reducing the employability gap by 20%. X educators hail: “NEP’s experiential shift is turning classrooms into incubators.”
This line chart tracks NEP-driven entrepreneurial exposure growth (2020-2025):
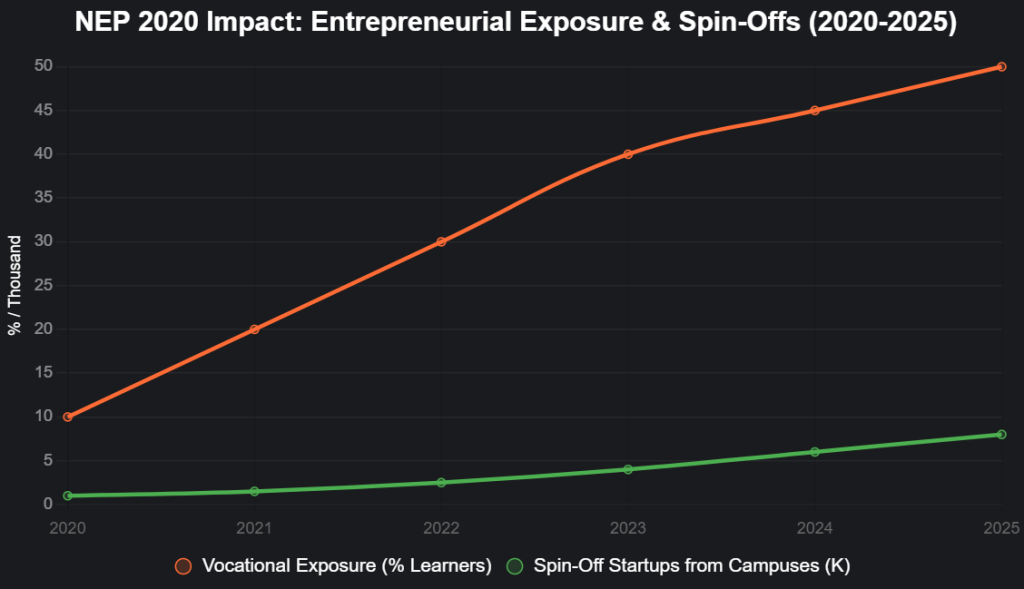
Source: UGC, DPIIT. 50% vocational by 2025 drives 8x spin-offs.
Core Changes: NEP’s Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Mindsets
NEP 2020’s reforms target curriculum, pedagogy, and infrastructure to instill risk-taking, creativity, and resilience.
1. Multidisciplinary and Flexible Curriculum
Rote learning yields to choice-based credits, blending arts, sciences, and vocational skills from Class 6—coding, AI, entrepreneurship mandatory. By 2025, 50% schools integrate internships, fostering problem-solving; IIT Madras’ curriculum revamp produced 41 pre-seed startups in Q3.
2. Experiential and Skill-Based Learning
Shift to project-based assessments and vocational exposure (50% learners by 2025) builds grit; AIM’s tinkering labs in 10,000 schools spark 2,500 innovators yearly. IIM Ahmedabad’s CIIE incubated 200 ventures via hands-on programs.
3. Teacher Training and Innovation Councils
4-year B.Ed. by 2030 equips educators for entrepreneurial pedagogy; Institution’s Innovation Councils (IICs) in 1,000+ colleges foster startups, per UGC. 2025: 80% teachers trained in critical thinking.
4. Incubation and Ecosystem Integration
700+ incubators via AIM link campuses to Startup India, with Rs 10 crore grants per center; BITS Pilani’s 900 spin-offs include 13 unicorns like Swiggy.
| Reform Pillar | Pre-NEP Issue | NEP 2020 Change | 2025 Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curriculum | Rote, siloed | Multidisciplinary, vocational | 50% learners skilled; 20% employability rise |
| Pedagogy | Exam-centric | Experiential, project-based | 40% critical thinking boost |
| Teacher Training | Inadequate | 4-year B.Ed., innovation focus | 80% trained; 30% better outcomes |
| Infrastructure | Limited labs | 2,500 tinkering labs | 10K spin-offs, 1.5M jobs |
Source: UGC, DPIIT.
Spotlight: Campuses Leading the Charge
- IIT Bombay’s SINE: 224 spin-offs, including ideaForge (IPO unicorn), via prototyping grants.
- BITS Pilani: 900 ventures, 13 unicorns (Swiggy, Groww), through Practice School internships.
- IIM Bangalore’s NSRCEL: 150+ startups like Razorpay ($7.5B), emphasizing entrepreneurial pedagogy.
Challenges: Implementation Hurdles
40% facilities underutilized due to teacher resistance and rural gaps; 55% awareness low in Tier-2. X: “NEP’s gold, but execution lags—train teachers first.” AICTE’s curricula and DST’s 5,000 incubators by 2030 counter this.
The Entrepreneurial Horizon: 1.25 Lakh Creators by 2030
NEP could nurture 1.25 lakh entrepreneurs, per state policies, rivaling global hubs. Founders: Mentor campus talent. Educators: Embrace experiential. India’s curriculum isn’t changing—it’s transforming mindsets. Forge the future, or fossilize the past.
social media : Facebook | X | Pinterest | Linkedin | Reddit
Last Updated on Saturday, October 25, 2025 6:53 pm by Entrepreneur Edge Team https://entrepreneuredge.in/